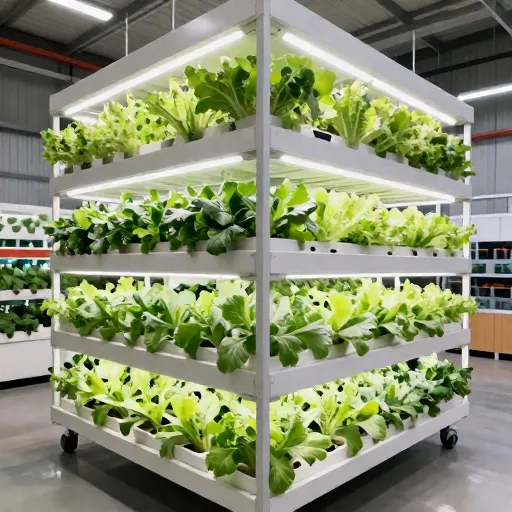
Develop an interactive report on urban farming innovations, covering vertical farming, hydroponics, and aquaponics. Include case studies demonstrating the potential of urban farming to address food security challenges in cities.
Urban Farming Innovations: Vertical Farming, Hydroponics, and Aquaponics
Urban farming is revolutionizing how cities approach food security by utilizing limited space and resources to produce fresh, local food. Key innovations include vertical farming, hydroponics, and aquaponics, each offering unique benefits and opportunities.
1. Vertical Farming
Overview:
Vertical farming involves growing crops in stacked layers, often using controlled environments such as LED lighting, climate regulation, and automated nutrient delivery to maximize yield per square foot. This method is space-efficient and can be set up indoors or on rooftops.
Benefits:
- Maximizes land use by growing upward instead of outward
- Year-round production independent of weather
- Reduced water usage compared to traditional farming
- Minimizes pesticide use and reduces transportation emissions
Case Study:
AeroFarms, Newark, NJ
AeroFarms uses aeroponic vertical farming to grow leafy greens in urban warehouses. They’ve succeeded in producing up to 390 times more crops per square foot than traditional field farming, while using 95% less water. AeroFarms supplies fresh greens to local grocery stores and restaurants, reducing food miles and boosting urban food resilience.
2. Hydroponics
Overview:
Hydroponics grows plants in nutrient-rich water solutions without soil. This system often uses less water and fewer chemicals, speeding up plant growth and enabling controlled nutrient delivery.
Benefits:
- Fast crop turnover and growth
- Efficient use of water and nutrients
- Can be deployed in small indoor spaces such as apartments or basements
- Reduces soil-borne disease risks
Case Study:
BrightFarms, multiple locations USA
BrightFarms designs hydroponic greenhouses near urban centers. Their model reduces supply chain times and delivers fresh, pesticide-free produce to supermarkets rapidly, lowering environmental impact and increasing access to fresh greens in food deserts.
3. Aquaponics
Overview:
Aquaponics combines fish farming (aquaculture) with hydroponics. Fish waste provides nutrients for plants, which in turn filter the water for fish. This symbiotic system creates a sustainable closed-loop ecosystem.
Benefits:
- Produces both protein (fish) and vegetables
- Reduces water consumption dramatically by recycling
- Creates a balanced, natural environment reducing need for chemical inputs
- Encourages local, circular food production
Case Study:
The Plant, Chicago, IL
The Plant is an industrial-scale aquaponics facility located in a repurposed meatpacking warehouse. They produce fish like tilapia alongside leafy greens and herbs, supported by renewable energy. This project is a prime example of turning industrial urban spaces into productive food hubs.
Urban Farming and Food Security
Cities face growing food security challenges due to population growth, climate change, and supply chain vulnerabilities. Urban farming innovations help address these by:
- Increasing local food production capacity
- Reducing dependence on long-distance transportation
- Providing fresher, more nutritious produce
- Creating green jobs and promoting community engagement
These innovative techniques demonstrate the potential for cities worldwide to transform unused spaces into vibrant food production facilities, enhancing resilience and sustainability.
Would you like visuals showing how these systems work or more detailed case studies?
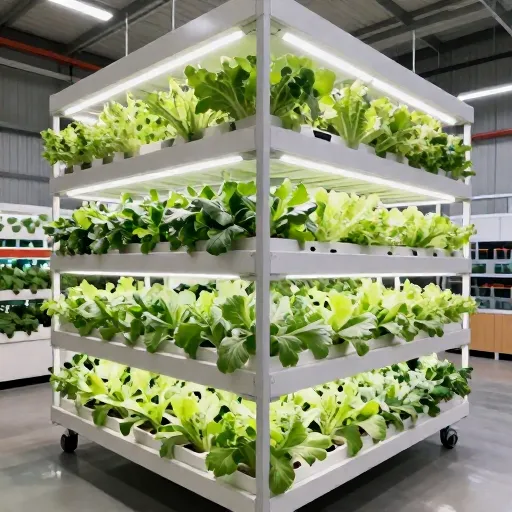

Show visuals of hydroponic systems
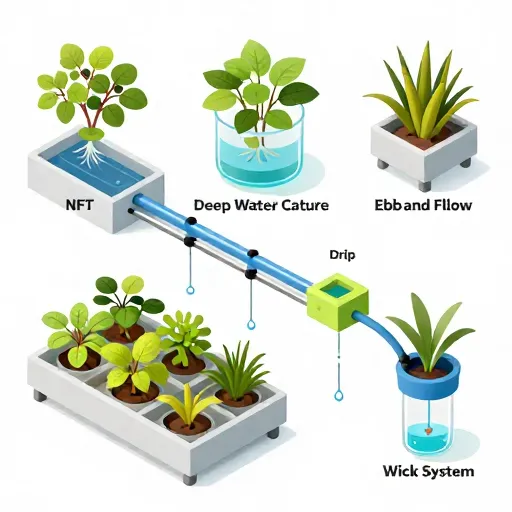
Here is a detailed visual overview of hydroponic systems commonly used in urban farming. These setups display different approaches to growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions without soil, perfect for compact urban spaces:
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): Thin film of nutrient solution flows over plant roots in a sloped channel.
- Deep Water Culture (DWC): Plants float on rafts with roots submerged in oxygenated nutrient water.
- Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain): Growing tray is periodically flooded with nutrient solution then drained.
- Drip System: Nutrient solution drips onto the base of each plant in containers.
- Wick System: Nutrients are drawn up by capillary action from a reservoir to the roots through a wick.
Each system optimizes water and nutrient use, space efficiency, and crop speed, making hydroponics ideal for urban farming.
Can you explain vertical farming technology in more detail?
Absolutely! Here’s a detailed explanation of vertical farming technology, highlighting how it transforms urban agriculture by stacking layers of crops vertically in controlled environments:
What is Vertical Farming Technology?
Vertical farming is an innovative method of growing crops in vertically stacked layers—often integrated into skyscrapers, warehouses, or shipping containers. This technique uses controlled-environment agriculture (CEA) technology to optimize plant growth by managing light, temperature, humidity, and nutrients.
Key Components of Vertical Farming Technology
1. Multi-layered Growing Systems:
- Crops are planted in trays or shelves arranged vertically. This maximizes production area in limited urban spaces, making it ideal for cities where land is scarce.
2. Artificial Lighting (LEDs):
- High-efficiency, full-spectrum LED lights replace or supplement sunlight. LEDs can be fine-tuned to emit specific light wavelengths ideal for photosynthesis, enhancing growth speed and yield.
3. Climate Control Systems:
- Temperature, humidity, CO2 levels, and airflow are precisely monitored and adjusted using HVAC systems and sensors. This creates optimal conditions year-round, regardless of external weather.
4. Automated Nutrient Delivery:
- Hydroponic, aeroponic, or other soilless systems deliver water and nutrients tailored to each crop’s needs, often automatically regulated with pumps and sensors.
5. Data & AI Integration:
- Sensors collect real-time data on plant health and environmental factors. Artificial intelligence (AI) analyzes this data to optimize resource use, predict growth cycles, and reduce waste.
How Vertical Farming Works
- Seeds are planted in growing media or directly in nutrient solutions.
- Layers of plants stacked vertically receive precise LED light and optimal climate.
- Automated systems deliver water and nutrients directly to roots.
- Data from sensors adjust light cycles, temperature, or watering schedules to maximize growth.
- Harvest is done continuously or in cycles, as the system supports rapid crop turnover.
Benefits of Vertical Farming Technology
- Space Efficiency: Produces large quantities on minimal land by expanding upward.
- Water Conservation: Uses up to 90% less water than traditional farming by recycling water in closed systems.
- Year-Round Production: Unaffected by seasonal changes or weather, ensuring consistent crop supply.
- Reduced Transportation: Grows food close to consumers, lowering greenhouse gas emissions from transport.
- Reduced Pesticides: Controlled environments reduce pest threats, minimizing or eliminating pesticide use.
Example: Vertical Farming in Action
Plenty, San Francisco, CA:
Plenty builds vertical farms inside warehouses using scalable layers and machine learning. Their farms produce thousands of tons of leafy greens annually with significantly less water, running almost pesticide-free and supporting local food security by shortening supply chains.
Would you like to see visuals explaining vertical farm stacks and lighting systems, or hear about the challenges facing this technology?
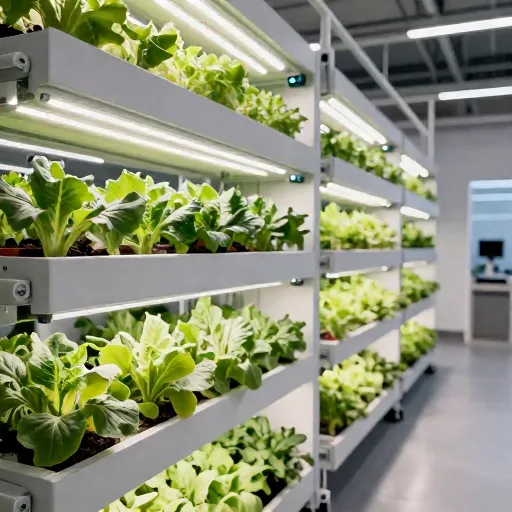

Show me visuals of vertical farming systems
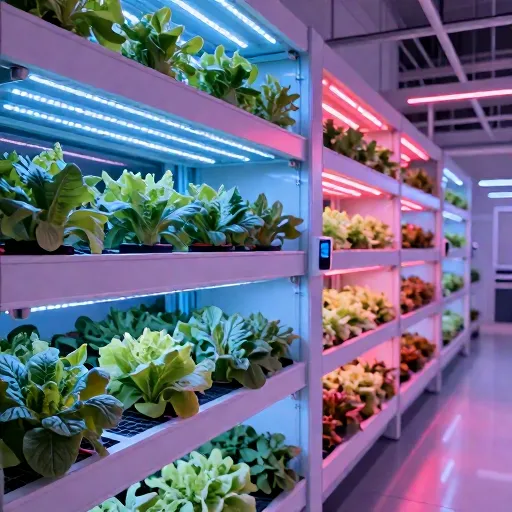
Here are some detailed visuals showcasing vertical farming systems in action. These images highlight the multi-layered stacks of crops, the advanced LED lighting, automated irrigation, and climate control setups used to optimize urban food production:
- Stacked Growing Layers: Rows of leafy greens growing in vertical racks inside a clean, modern warehouse environment.
- LED Lighting: Bright, full-spectrum LED panels positioned above each layer to simulate sunlight and promote photosynthesis.
- Irrigation & Nutrient Delivery: Pipes and tubing supplying a controlled hydroponic or aeroponic nutrient solution to plants.
- Climate Control Systems: Sensors and vents visible in the background managing airflow, temperature, and humidity.
These systems efficiently produce food in limited urban spaces while ensuring sustainability and high yields.

What are the challenges of scaling vertical farms?
Scaling vertical farms presents several challenges despite their promising potential to improve urban food security. Here are some of the key hurdles:
1. High Initial Capital Investment
- Setting up vertical farms requires significant upfront costs for real estate, advanced lighting (LEDs), climate control systems, automation, and sensors. This can be a barrier, especially for smaller startups or communities.
2. Energy Consumption
- Artificial lighting and climate control systems consume a lot of energy. Ensuring energy efficiency or integrating renewable energy is critical but can be complicated and costly.
3. Technical Complexity
- Maintaining precise environmental conditions requires sophisticated technology, ongoing monitoring, and skilled staff. Technical failures can quickly affect crop health.
4. Crop Variety Limitations
- Vertical farms are typically optimized for leafy greens and herbs. Scaling to staple crops like grains or root vegetables is more difficult due to space, growth cycle, and weight constraints.
5. Water and Nutrient Management
- While vertical farms use less water overall, effective recycling and managing nutrient solutions to avoid disease outbreaks is complex at larger scales.
6. Economic Viability and Market Demand
- Producing high-value crops is essential to recoup costs. Ensuring consistent demand and competitive pricing against traditional farms and imported produce is a continuous challenge.
Despite these challenges, ongoing technological advances and policy support are helping reduce barriers and improve vertical farming scalability.
Here’s a visual illustrating these challenges within the context of a vertical farm setup:

How do renewable energy sources integrate with vertical farms?
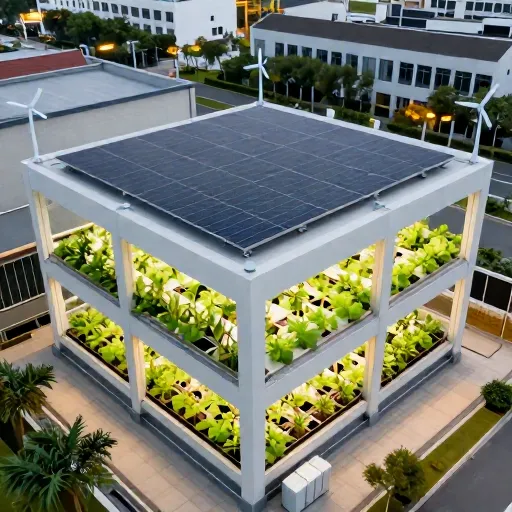
Renewable energy integration is essential for making vertical farming more sustainable and cost-effective, as these farms can be energy-intensive due to their reliance on artificial lighting and climate control systems. Here’s how renewable energy sources typically work with vertical farms:
1. Solar Power
- Solar panels installed on rooftops, nearby land, or on vertical farm buildings generate electricity to power LED lighting, pumps, sensors, and HVAC systems.
- Excess solar energy can be stored in batteries to ensure consistent power supply during nighttime or cloudy days.
2. Wind Energy
- Where feasible, small-scale wind turbines can supplement energy needs, especially in windy urban locations or on farm rooftops.
- Wind energy reduces reliance on grid electricity and fossil fuels.
3. Energy Storage Systems
- Battery storage systems store renewable-generated electricity to provide a stable power supply, balancing periods of low generation.
- Advanced energy management platforms optimize when and how energy is consumed.
4. Energy Efficiency Measures
- Vertical farms integrate energy-efficient LED lights and smart climate control to reduce overall consumption, maximizing the benefits of the renewable energy produced.
5. Combined Systems
- Some vertical farms combine multiple renewable sources (solar, wind) with energy-efficient technology and grid power as a backup to create a resilient and near-zero carbon footprint farm.
Benefits of Renewable Energy Integration
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions linked with farming operations.
- Lowers long-term operational costs by decreasing electricity bills.
- Strengthens energy independence and resilience against grid disruptions.
This visual showcases a sustainable vertical farm powered by solar panels on the rooftop and wind turbines on the building perimeter, with integrated battery storage and energy-efficient farming technologies.

What types of crops are best suited for vertical farming?
#newtechnology #stories #urbanfarming #World






